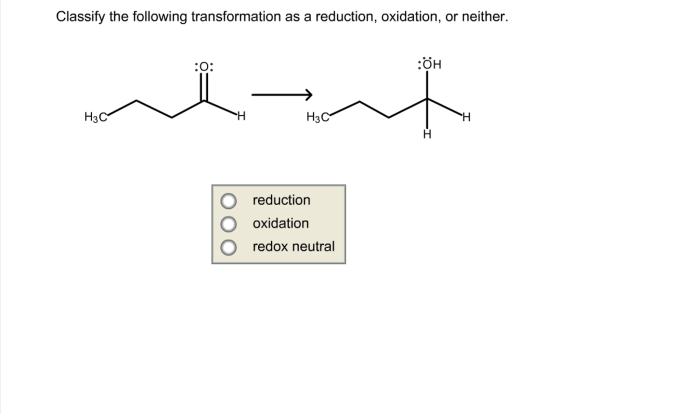
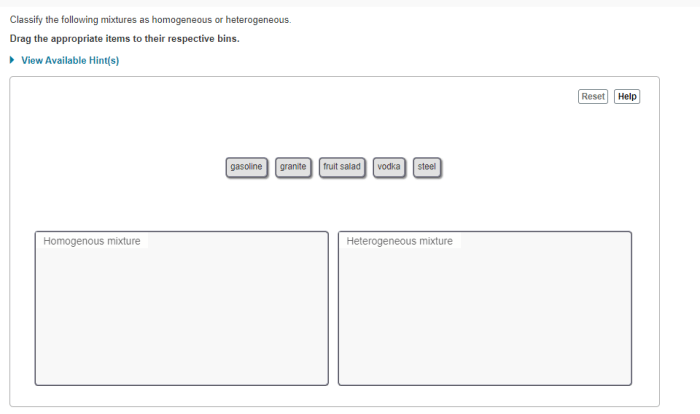
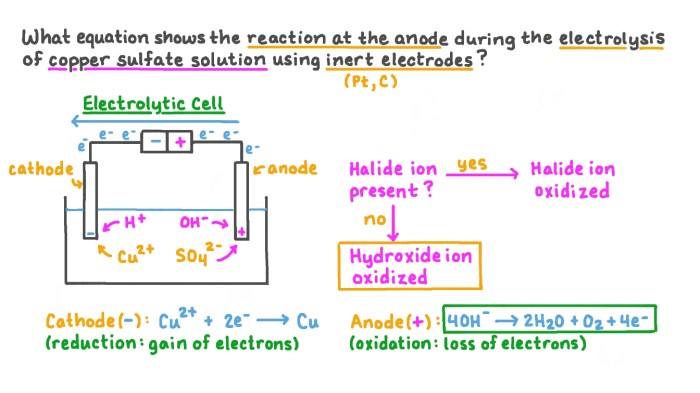
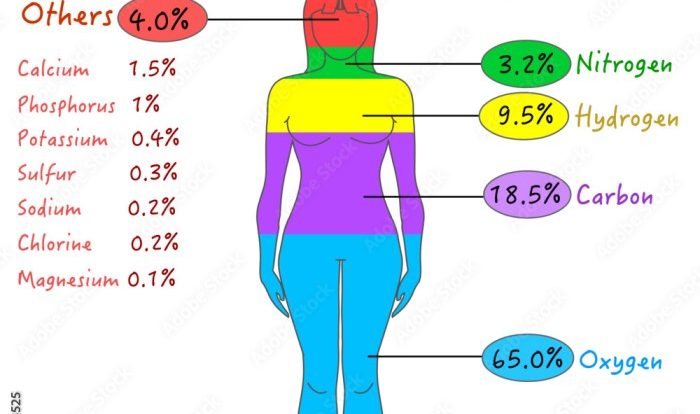
Modern chemistry holt rinehart and winston – Modern Chemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Holt Rinehart and Winston Curriculum delves into the fundamental principles of chemistry, exploring the structure and bonding of atoms and molecules, chemical reactions and energy, equilibrium and dynamic processes, acids, bases, and solutions, and organic chemistry.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the subject, making it an invaluable resource for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the intricacies of modern chemistry.
Through clear and concise explanations, engaging examples, and illustrative diagrams, this guide unravels the complexities of chemical concepts, making them accessible to readers of all levels. It serves as a valuable companion to the Holt Rinehart and Winston curriculum, providing supplemental information and insights that enhance the learning experience.
1. Key Concepts in Modern Chemistry

Modern chemistry is founded on a set of fundamental principles that have revolutionized our understanding of the world around us. These principles include:
Quantum Mechanics:This theory describes the behavior of atoms and molecules at the subatomic level, providing a framework for understanding their properties and interactions.
Thermodynamics:This branch of chemistry studies the energy changes that accompany chemical reactions, allowing us to predict reaction outcomes and design efficient processes.
Kinetics:This field examines the rates of chemical reactions, providing insights into reaction mechanisms and enabling us to control reaction rates for practical applications.
Molecular Geometry:This concept describes the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in molecules, influencing their physical and chemical properties.
2. Structure and Bonding in Modern Chemistry
Chemical bonding is the force that holds atoms together to form molecules. There are several types of chemical bonds, including:
- Covalent Bonds:These bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, resulting in the formation of stable molecules.
- Ionic Bonds:These bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, creating charged ions that are held together by electrostatic forces.
- Metallic Bonds:These bonds involve the sharing of electrons among many metal atoms, resulting in the formation of extended metallic structures.
Molecular geometry is determined by the arrangement of electron pairs around the atoms in a molecule. This geometry influences the molecule’s physical and chemical properties, such as its reactivity and solubility.
3. Chemical Reactions and Energy

Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms and molecules to form new substances. These reactions can be classified as either:
- Exothermic Reactions:These reactions release energy in the form of heat or light.
- Endothermic Reactions:These reactions require energy input to occur.
The rate of a chemical reaction is determined by several factors, including the concentration of reactants, temperature, and the presence of a catalyst.
4. Equilibrium and Dynamic Processes
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of reactants and products do not change over time. This state is reached when the forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates.
Factors that affect equilibrium include:
- Temperature:Increasing temperature can shift the equilibrium towards the products of an endothermic reaction and towards the reactants of an exothermic reaction.
- Concentration:Increasing the concentration of reactants shifts the equilibrium towards the products, while increasing the concentration of products shifts the equilibrium towards the reactants.
- Pressure:Increasing pressure shifts the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
5. Acids, Bases, and Solutions: Modern Chemistry Holt Rinehart And Winston

Acids and bases are two important classes of compounds that have distinct properties. Acids are characterized by their ability to donate protons (H+), while bases are characterized by their ability to accept protons.
The strength of an acid or base is measured by its pH value. A pH value of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while a pH value less than 7 indicates an acidic solution and a pH value greater than 7 indicates a basic solution.
6. Organic Chemistry

Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon. These compounds are found in all living organisms and are essential for life.
Organic compounds can be classified into various functional groups, each with its own characteristic properties. Some common functional groups include:
- Alkanes:These are hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms.
- Alkenes:These are hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
- Alkynes:These are hydrocarbons with at least one triple bond between carbon atoms.
- Alcohols:These are compounds that contain a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
- Carboxylic Acids:These are compounds that contain a carboxyl (-COOH) group.
FAQ Resource
What are the key concepts covered in Modern Chemistry: A Comprehensive Guide to the Holt Rinehart and Winston Curriculum?
This guide covers the fundamental principles of modern chemistry, including the structure and bonding of atoms and molecules, chemical reactions and energy, equilibrium and dynamic processes, acids, bases, and solutions, and organic chemistry.
How does this guide complement the Holt Rinehart and Winston curriculum?
This guide provides supplemental information and insights that enhance the learning experience by offering clear and concise explanations, engaging examples, and illustrative diagrams.
Is this guide suitable for students of all levels?
Yes, this guide is written in a clear and accessible style, making it suitable for students of all levels, from beginners to advanced learners.