All of the following are characteristics of metamorphic rocks except: foliation, banding, schistosity, and extrusive texture. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are subjected to high heat and pressure, causing them to change their physical and chemical properties. These changes can result in the formation of new minerals, the alteration of existing minerals, and the development of new textures.
The distinctive physical properties of metamorphic rocks, such as foliation, banding, and schistosity, are the result of the high temperatures and pressures that they are subjected to. Foliation is the alignment of platy minerals, such as mica, into parallel layers.
Banding is the alternating layers of light and dark minerals. Schistosity is the foliated texture that is produced when platy minerals are aligned in a parallel fashion.
Metamorphic Rocks: Physical Characteristics, Processes, Composition, and Textures
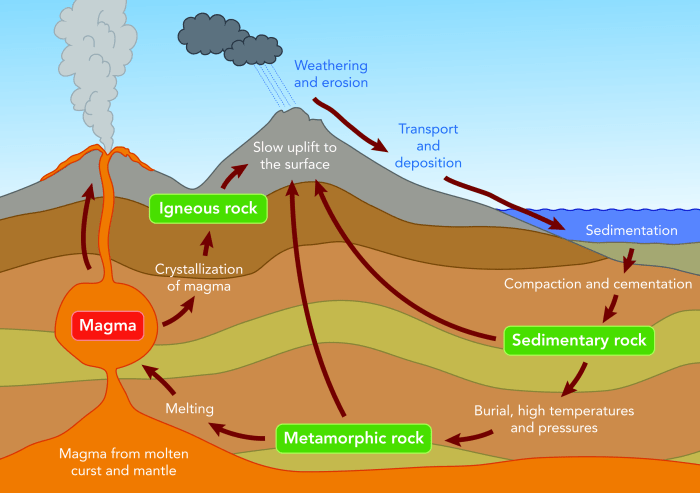
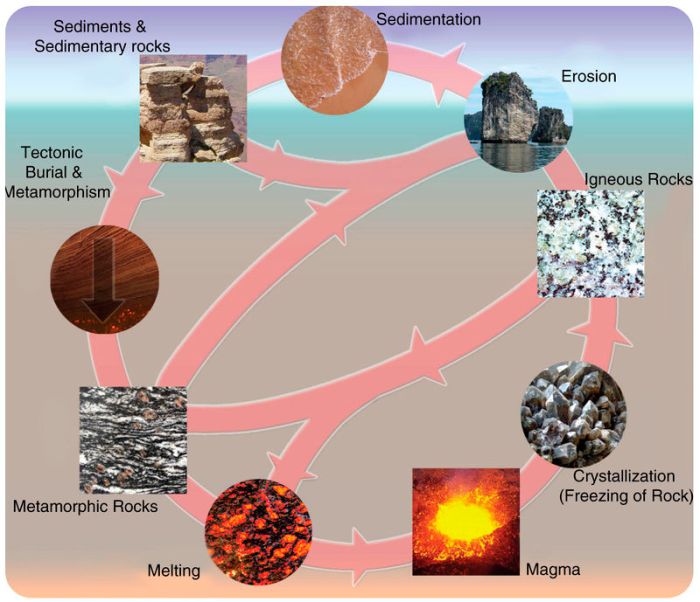
Metamorphic rocks are formed when pre-existing rocks undergo significant changes in temperature, pressure, or chemical composition. These changes can occur deep within the Earth’s crust during tectonic processes such as mountain building or when rocks come into contact with hot magma.
Physical Characteristics of Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rocks are often characterized by their distinct physical properties, which differ from those of igneous and sedimentary rocks. These properties include:
- Foliation:Foliation is a layering or banding of minerals within a metamorphic rock. It is caused by the alignment of minerals under pressure during metamorphism.
- Banding:Banding is a similar layering or banding of minerals, but it is caused by differences in mineral composition rather than mineral alignment.
- Schistosity:Schistosity is a foliated texture in which the minerals are arranged in parallel layers. This texture is typically found in metamorphic rocks that have undergone high pressure and temperature.
Metamorphic Processes
Metamorphic rocks are formed through a variety of metamorphic processes, including:
- Contact metamorphism:Contact metamorphism occurs when rocks come into contact with hot magma. The heat from the magma causes the rocks to recrystallize, forming new minerals.
- Regional metamorphism:Regional metamorphism occurs over large areas of the Earth’s crust, typically during mountain building. The heat and pressure associated with mountain building cause the rocks to recrystallize and form new minerals.
- Hydrothermal metamorphism:Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs when hot, water-rich fluids circulate through rocks. These fluids can cause the rocks to recrystallize and form new minerals.
Composition of Metamorphic Rocks, All of the following are characteristics of metamorphic rocks except
The composition of metamorphic rocks depends on the original rock material and the metamorphic conditions. Common minerals found in metamorphic rocks include:
- Quartz:Quartz is a common mineral in metamorphic rocks. It is hard and resistant to weathering.
- Feldspar:Feldspar is a group of minerals that are common in metamorphic rocks. Feldspars are typically white or pink.
- Mica:Mica is a group of minerals that are common in metamorphic rocks. Micas are typically platy or flaky.
Textures of Metamorphic Rocks
The texture of a metamorphic rock is determined by the metamorphic conditions and the original rock material. Common textures of metamorphic rocks include:
- Gneissic:Gneissic texture is characterized by alternating bands of light and dark minerals. This texture is typically found in metamorphic rocks that have undergone high pressure and temperature.
- Schistose:Schistose texture is characterized by parallel layers of minerals. This texture is typically found in metamorphic rocks that have undergone high pressure and temperature.
- Granoblastic:Granoblastic texture is characterized by interlocking grains of minerals. This texture is typically found in metamorphic rocks that have undergone high temperature.
FAQ: All Of The Following Are Characteristics Of Metamorphic Rocks Except
What is the difference between foliation and banding?
Foliation is the alignment of platy minerals, such as mica, into parallel layers. Banding is the alternating layers of light and dark minerals.
What is the difference between schistosity and foliation?
Schistosity is the foliated texture that is produced when platy minerals are aligned in a parallel fashion. Foliation is the general term for the alignment of platy minerals into parallel layers.
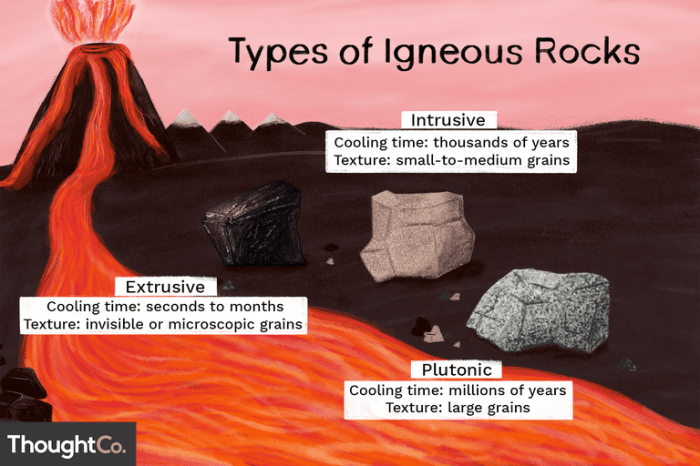
What is the difference between extrusive and intrusive texture?
Extrusive texture is a texture that is produced when lava cools quickly on the Earth’s surface. Intrusive texture is a texture that is produced when magma cools slowly beneath the Earth’s surface.